在海水循环养殖系统(RAS)中,积累的硝酸盐(NO3--N)对养殖鱼类表现出了慢性毒性,应用反硝化技术可有效去除NO3--N。此外,RAS中养殖固体废物(MSW)的存在对养殖生物、水生环境等也具有消极影响。因此,本研究以MSW产酸发酵液作为碳源对RAS废水进行生物反硝化处理,并从COD/NO3--N和HRT两方面对脱氮效果进行优化,以促进养殖水中NO3--N的去除,解决MSW的处理问题,为RAS在经济和环境方面的可持续发展提供理论指导。
研究结果表明,以MSW产酸发酵液作为碳源,异养反硝化的最佳COD/NO3--N为8,HRT为6h, NO3--N的去除率分别为97.8%和94.2%。MSW产酸发酵液中,VFAs的利用效率高于碳水化合物和蛋白质的利用效率。与较低的COD/NO3--N和HRT相比,在最佳的COD/NO3--N和HRT条件下Thauera、Aequorivita、Dokdonella、Denitratisoma和Nitrincola等反硝化细菌得到富集,而Simplicispira等反硝化细菌丰富度下降,这表明通过优化COD/NO3--N和HRT,反应器内微生物群落得到选择性富集,因而显著提高了反硝化的脱氮效果。
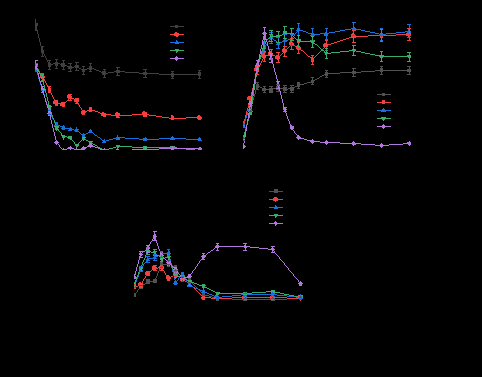
Fig. 1. Profile of NO3--N, NO2--N and NH4+-N reduction during heterotrophic denitrification process using MSW fermentation liquid as carbon source at different C/Ns.
图1.不同COD/NO3--N条件下,以养殖废弃物发酵液为碳源的异养反硝化过程中NO3--N, NO2--N和NH4+-N去除曲线。
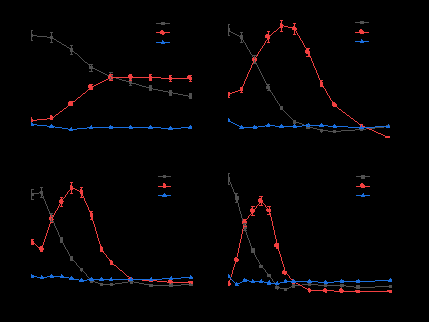
Fig. 2. Profile of NO3--N, NO2--N and NH4+-N reduction during heterotrophic denitrification process using MSW fermentation liquid as carbon source at different HRTs.
图2.不同HRT条件下,以养殖废弃物发酵液为碳源的异养反硝化过程中NO3--N, NO2--N和NH4+-N去除曲线。
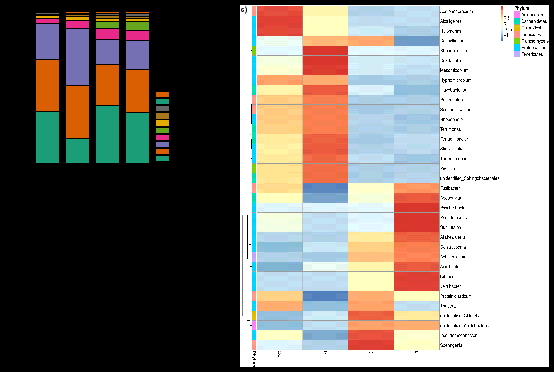
Fig. 3. The microbial community compositional structures. The relative abundance at phylum level (a) and genus level (b) in four sludge samples; Cluster heatmap at genus level in four sludge samples (c).
图3. 微生物群落组成结构。污泥样品中的微生物在门水平(a)和属水平(b)上的相对丰度;污泥样品中的微生物在属水平上的聚类热图(c)。
论文引用:
Yedong Gao, Liang Guo⁎, Mengyu Shao, Fawen Hu, Guangce Wang, Yangguo Zhao, Mengchun Gao, Chunji Jin, Zonglian She. Heterotrophic denitrification strategy for marine recirculating aquaculture wastewater treatment using mariculture solid wastes fermentation liquid as carbon source: Optimization of COD/NO3--N ratio and hydraulic retention time. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 304: 122982.

