2017年1月4日,地学领域权威期刊Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences发表了题为“Contributions of physical and biogeochemical processes to phytoplankton biomass enhancement in the surface and subsurface layers during the passage of Typhoon Damrey”的研究论文,定量解析了台风“戴维”经过南海时表层和次表层初级生产过程的变化机制,为充分认识台风对海洋生物地球化学循环过程的影响提供理论依据。
本研究在南海北部海区建立了垂直一维的物理-生物耦合的生态系统动力学模型,模拟了海洋生态系统对2005年9月的台风“戴维”的响应情况。模拟结果显示,台风过境引起海表叶绿素浓度迅速从0.07 增长到 0.17 mg m-3,继而在台风过境之后缓缓增长到其峰值0.61 mg m-3。在海洋次表层,叶绿素浓度的反应与表层不同。当台风过境时,其叶绿素浓度迅速从0.34 降低到 0.17 mg m-3;台风过境之后,叶绿素浓度缓缓增加到0.71 mg m-3。定量计算的结果表明,台风过境时海表的叶绿素浓度急增和次表层的骤降,是台风引起的强物理混合的结果;而台风过境之后,表层和次表层叶绿素浓度的缓慢增长主要是由于生物过程导致;而且次表层增长的持续时间要长于表层。台风“戴维”引起初级生产力的增量为6.5×103 mg C m-2,约占全年初级生产力的14%。
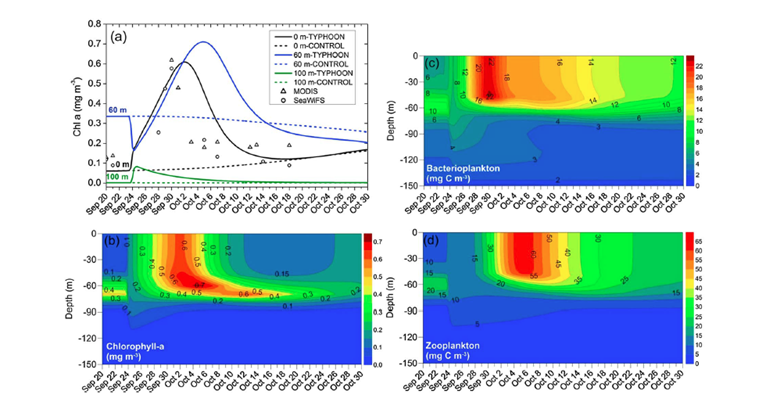
图1 模型模拟结果及与卫星观测结果的对比
Figure 1 (a) Time series of Chl a (mg m-3) in the surface, subsurface, and deep layers from 20 September to 30 October according to the CONTROL (dash line) and TYPHOON (solid line) simulations, and satellite sea surface Chl a data acquired from MODIS (dark triangles) and SeaWiFS (dark circles). Depth-time plots of modeled (b) Chl a, (c) bacterioplankton (mg C m-3), and (d) zooplankton (mg C m-3) from 20 September to 30 October in the TYPHOON simulation.
该研究主要由海洋环境与生态教育部重点实验室高会旺教授团队完成,硕士研究生潘珊珊为第一作者,史洁副教授为通讯作者,并得到国家重大科学研究计划(2014CB953702)及国家自然科学基金(41506013, 41406010)的资助。
论文引用:
Pan, S., Shi, J.*, Gao, H., Guo, X., Yao, X., Gong, X. (2017). Contributions of physical and biogeochemical processes to phytoplankton biomass enhancement in the surface and subsurface layers during the passage of Typhoon Damrey. Journal of Geophysical Research, 122(1), 212-229.
论文链接:
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2016JG003331
通讯员:
潘珊珊 张潮

